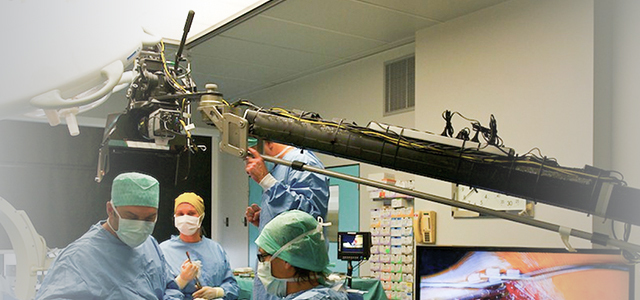
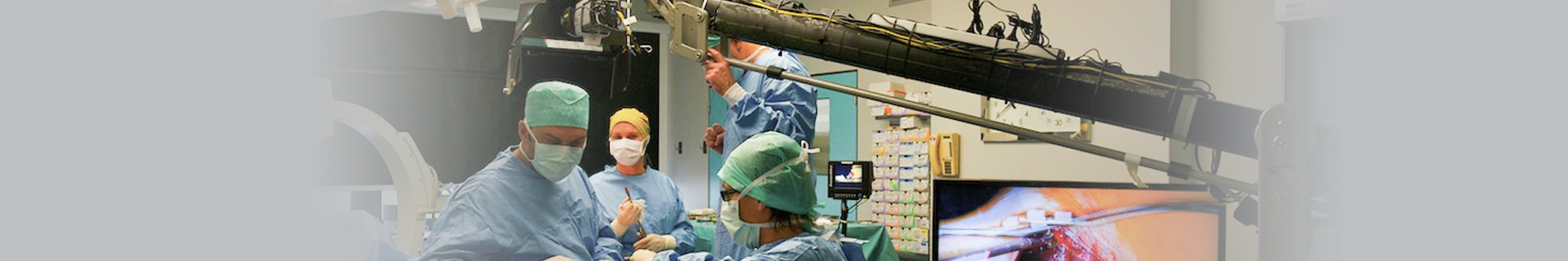
Laparoscopic minimally invasive radical prostatectomy in combination with urology and anesthesia
Recently, the urology team of Yan’an Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Yan’an Branch of Peking University Third Hospital) collaborated with the Department of Anesthesiology and Surgery to carry out difficult and complex laparoscopic minimally invasive radical prostatectomy, marking a new breakthrough in the urology surgery technology of Yan’an Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital.

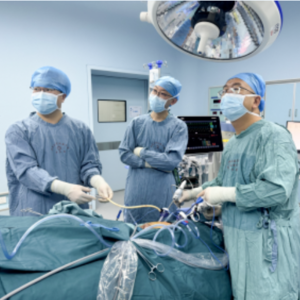
Director Guo Wei (first from right) and Professor Xu Chuxiao (second from left) are undergoing surgery
Mr. Cao has been troubled by symptoms of frequent urination and difficulty urinating for many years, but he has never taken them to heart. One day before admission, Mr. Cao experienced lower abdominal distension and inability to urinate.
After admission, a comprehensive prostate tumor specific antigen (PSA) test was performed, indicating a total PSA of 13.8 ng/mL and a free PSA of 2.31 ng/mL. Further improvement of prostate magnetic resonance imaging revealed significant hyperplasia of the prostate, prominent protrusion of the middle lobe into the bladder, abnormal signal nodules visible in the upper left and lower right central glands, high signal intensity on DWI, decreased ADC value, and a PI-RADS score of 3.

MR image of the patient’s prostate (red arrow indicates protruding middle lobe of the prostate, yellow arrow indicates suspicious tumor area on imaging)
Xu Chuxiao, academic director of the Department of Urology stationed in Beijing, and Guo Wei, director of the Department of Urology, quickly organized a general discussion to comprehensively evaluate the patient’s condition. Considering the high possibility of prostate hyperplasia combined with prostate cancer, in order to further clarify the diagnosis, it is recommended to undergo prostate puncture biopsy. The urology team fully communicated with the patient and their family members about the condition, and after obtaining informed consent, performed ultrasound-guided transperineal cognitive fusion targeted prostate puncture biopsy. The pathological diagnosis is prostate acinar adenocarcinoma, with a Gleason score of 3+3=6 points.
Xu Chuxiao, the academic director of the Department of Urology stationed in Beijing, and Guo Wei, the director of the Department of Urology, organized a general discussion again regarding the condition: the patient was diagnosed with prostate cancer, with a Gleason score of 3+3=6 points, clinical staging considered cT2N0M0, total PSA of the patient was 13.8 ng/mL, and the prognosis was classified as medium risk. It is recommended to carry out laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection. During preoperative discussions, the urology team combined the patient’s condition to conduct predictive analysis and emergency plans for possible intraoperative situations.
Subsequently, another difficult problem was presented to the doctor. The patient has been smoking for a long time and has varying degrees of emphysema in both lungs, as well as atrial arrhythmias. Considering the difficulty of the surgery in this case, the time has been extended compared to conventional surgery, and the risk of postoperative pulmonary accidents is increased. After thorough evaluation by the Anesthesiology and Surgery Department of Yan’an Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, a detailed and comprehensive anesthesia plan has been developed based on the specific situation of the patient.

Prostate gross pathological specimen (left): The patient’s incision healed well after surgery, with the maximum incision only 3 cm (right)
After thorough and meticulous preoperative preparation, with the support of the Department of Anesthesiology and Surgery, the laparoscopic minimally invasive radical prostatectomy combined with pelvic lymph node dissection was successfully performed by Xu Chuxiao, the academic director of the Department of Urology stationed in Beijing, and Guo Wei, the director of the Department of Urology.
Thanks to the meticulous preoperative general practitioner discussion, despite encountering many difficulties such as "large and obvious protrusion of the middle lobe into the bladder", "severe adhesion around the prostate", and "complex reconstruction of the bladder neck" during the surgery, the urology team remained steadfast and followed the concept of layered surgery to overcome numerous difficulties. They completely removed the prostate and seminal vesicles, and reconstructed the bladder neck in a "fish mouth like" manner, perfectly matching the urethra and bladder neck, The water injection test showed no leakage at the anastomotic site, and the bilateral pelvic lymph nodes were completely cleaned.
Less intraoperative bleeding and smooth patient recovery.
Introduction by Director Guo Wei, Director of Urology Department:
Prostate cancer is one of the most common tumors of the genitourinary system in China, and its incidence rate is increasing year by year.
Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy has always been a highly challenging surgery that tests the skills of urologists. The difficulty lies in the fact that the prostate is located in the small pelvis at the lowest point of the human body, with a narrow operating space and a dense network of blood vessels and important nerves around it. It is adjacent to the rectum at the back, and even a slight mistake may damage the surrounding blood vessels, nerves, or rectum. Therefore, this surgical technique is a comprehensive test of various surgical techniques and belongs to one of the most difficult level four surgeries in urology.
This article is reprinted from "Dingxiangyuan"
Surgerycast
Shanghai Headquarter
Address: Room 201, 2121 Hongmei South Road, Minhang District, Shanghai
Tel: 400-888-5088
Email: surgerycast@qtct.com.cn
Beijing Office
Address: room 709, No.8, Qihang international phase III, No.16, Chenguang East Road, Fangshan District, Beijing
Tel: 13331082638( Liu )
Guangzhou Office
Address: No. 15, Longrui street, longguicheng, Taihe Town, Baiyun District, Guangzhou
Tel: 13302302667 ( Ding )